Explaining the cloud computing and its advantages
Cloud computing has ushered in a new era of digital innovation, transforming the way businesses operate and individuals interactions.
In an era defined by technological advancements, one term that has gained substantial prominence is "cloud computing."
It has transformed the way businesses operate, individuals interact with technology, and organizations store and process data.
In this blog post, we'll explore the concept of cloud computing and delve into its myriad advantages that have reshaped the digital landscape.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, at its core, is a revolutionary paradigm that allows users to access and utilize computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more, over the internet (the "cloud"). This shift from traditional on-premises computing to the cloud has redefined how individuals and businesses approach technology.
The cloud infrastructure is typically provided and maintained by third-party cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and many others. Users can access these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, offering scalability and flexibility like never before.
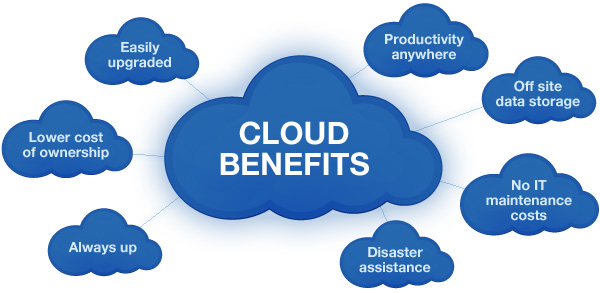
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Cost-EfficiencyOne of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its cost-efficiency. Traditional IT infrastructure often requires significant upfront investments in hardware and software, along with ongoing maintenance expenses. Cloud computing eliminates these capital expenditures by offering a pay-as-you-go model. Users only pay for the resources they consume, reducing operational costs and making technology accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- Scalability and FlexibilityThe cloud provides unparalleled scalability. Businesses can easily scale up or down their resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost control. Whether you need to accommodate a sudden influx of users, run data-intensive simulations, or simply expand your storage capacity, cloud computing allows you to do so with minimal effort.
- Accessibility and Remote WorkCloud computing facilitates remote work and collaboration. With cloud-based applications and data storage, employees can access their work from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility has become especially valuable in recent times, enabling organizations to adapt to remote work environments swiftly.
- Reliability and RedundancyLeading cloud providers invest heavily in redundancy and failover mechanisms, ensuring high availability and data reliability. Data is typically stored across multiple data centers in geographically diverse locations, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
- Security and ComplianceCloud service providers implement robust security measures to protect data and applications. They often have dedicated security teams and compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements. Additionally, cloud providers regularly update and patch their systems to address security vulnerabilities, reducing the burden on users.
- Automatic Updates and MaintenanceCloud providers handle software updates and maintenance, freeing users from the responsibility of managing and patching their infrastructure. This ensures that users always have access to the latest features and security enhancements without the hassle of manual updates.
- Resource OptimizationCloud computing allows for resource optimization through features like auto-scaling and load balancing. These tools automatically allocate resources based on workload, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Innovation and Competitive AdvantageCloud computing provides access to cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. This democratization of technology empowers businesses to innovate and gain a competitive edge without massive investments in specialized hardware and expertise.
- Environmental SustainabilityBy sharing and optimizing resources, cloud computing can be more environmentally friendly compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. Cloud providers often use energy-efficient data centers and implement green initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Global ReachCloud computing enables businesses to expand their reach globally without the need to set up physical infrastructure in multiple locations. This is especially beneficial for companies looking to tap into international markets.
Real-World Examples of Cloud Computing
To better understand the impact of cloud computing, let's explore a few real-world examples:
- Netflix: This popular streaming service relies on cloud computing to deliver content to millions of viewers worldwide. By using AWS, Netflix can scale its infrastructure to handle peak demand during popular shows and ensure a seamless streaming experience for users.
- Airbnb: Airbnb uses cloud computing to manage its vast database of listings, bookings, and user profiles. The company leverages AWS to handle traffic spikes during peak booking seasons, ensuring that their platform remains responsive and available.
- NASA: Even organizations like NASA benefit from cloud computing. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory uses AWS to process and store data from various missions, such as the Mars rovers. The cloud's scalability and reliability are crucial for handling the massive amounts of data generated by space exploration.
- Startups: Cloud computing has lowered the barriers to entry for startups and small businesses. Companies like Slack and Dropbox were able to rapidly scale their services without the need for large upfront investments in infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, it's important to be aware of potential challenges and considerations:
- Data Security: Despite robust security measures, the cloud is not immune to security breaches. Organizations must implement their security protocols and encryption practices to protect sensitive data.
- Data Transfer Costs: Moving large volumes of data in and out of the cloud can incur additional costs. It's essential to plan and optimize data transfer to minimize expenses.
- Vendor Lock-In: Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be complex and costly. Organizations should carefully consider vendor lock-in and explore strategies for data portability.
- Compliance and Data Sovereignty: Depending on your industry and location, you may have specific compliance requirements regarding data storage and processing. Ensure your chosen cloud provider can meet these requirements.
- Resource Monitoring: While the pay-as-you-go model is cost-effective, it requires diligent monitoring to prevent unexpected cost overruns. Implement resource tracking and budgeting tools to manage expenses effectively.
Cloud computing has ushered in a new era of digital innovation, transforming the way businesses operate and individuals interact with technology.
Its advantages, including cost-efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and security, have made it an indispensable tool in today's interconnected world.
As organizations continue to harness the power of the cloud, we can expect even more groundbreaking developments and innovations in the years to come.
Embracing cloud computing is not just a technological choice; it's a strategic decision that can propel businesses to new heights in the digital age.
What's Your Reaction?



















